The Zerofox Syndicate
Asmtutor X64_86 lesson 2
2022-06-06Disclaimer
These posts are heavily based on lessons that DGivney published on asmtutor.com.
I just wanted to port his lessons to x64 as an exercise for myself and put them somewhere online. Credit should still go to @DGiveny for putting his work online.
Lesson 2: Stopping the program
segmentation faults
If we do not tell the kernel that our program has finished, it is going to keep running until it runs into an error. In our hello world example that error comes into the form of a segmentation fault.
A segmentation fault occurs when our program tries to access memory it is not allowed to access. Trying to write to the 0 address for example will yield a segmentation fault. This is likely to occur when the computer tries to the memory that comes after the hello world instructions that we provided.
Exit codes
The syscall to correctly terminate a program on Linux is SYS_EXIT and we
trigger it by putting the code 60 in the rax register.
It takes one argument, that we have to put in rdi, the exit code.
Exit codes are commonly used to indicate whether a program was successful in
its operation. An exit code of 0 indicates a success, and any other exit code
usually indicates a failure.
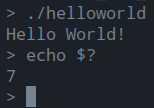
In the Bash shell, the exit code of a program is stored in the special variable
$? right after executing it.
You can view it with echo $?. This of course only works
once, as soon as you have executed echo $? the special variable $? will
contain the exit code of the echo command.
Let’s get into the code
Let’s add the code to cleanly exit our hello world example.
First we need to put 60 in the rax register so that the OS knows we want to
invoke the SYS_EXIT syscall and then we put our exit code into rdi.
; Hello World Program - asmtutor.com
; Compile with: nasm -f elf64 helloworld.asm
; Link with: ld -m elf_x86_64 helloworld.o -o helloworld
; Run with: ./helloworld
SECTION .data
msg db 'Hello World!', 0Ah ; assign msg variable with your message string
SECTION .text
global _start
_start:
mov rax, 1 ; invoke SYS_WRITE (kernel opcode 1)
mov rdi, 1 ; file descriptor to write to. STDOUT in this case
mov rsi, msg ; move the memory address of our message string into ecx
mov rdx, 13 ; number of bytes to write - one for each letter plus 0Ah (line feed character)
syscall
mov rax, 60 ; invoke SYS_EXIT
mov rdi, 0 ; exit with exit code 0
syscall
As an exercise, modify the code and let the program exit with exit code 7.